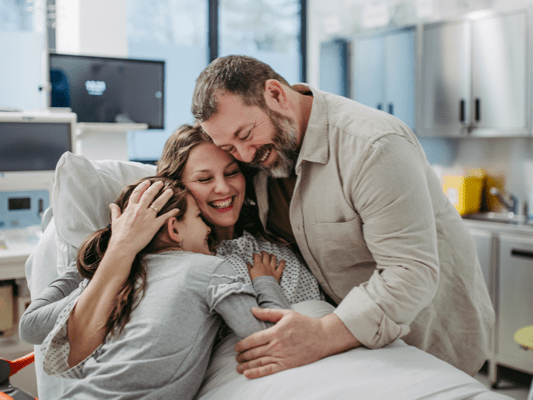
When a patient arrives at the hospital with an infection, the key to treating them and getting them out is the speed at which they get the right antibiotics.

Broad-spectrum antibiotics are often prescribed to cover a wide range of infections when the specific infecting pathogen has not been quickly identified. This practice, while intended to ensure immediate treatment, can inadvertently foster antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The extensive use of these powerful medications, even when they may not be needed, underscores the critical challenge of balancing immediate treatment needs with the risk of escalating resistance.

Currently, the antimicrobial susceptibility test, the so called antibiogram, requires growing a culture for 1-2 days in order to to identify the pathogen. The precise timescale depends on the type of bacteria. After this, an additional 12–24 hours are needed to conduct an antibiotic sensitivity screen. In the case of slow growing bacteria, e.g. M. tuberculosis, such a test may take up a full month to complete.

It is estimated that at least 700 000 people die every year from the infections caused by antibiotic resistant bacteria. If no action is taken the death toll may reach 10 million a year by 2050. It is more than the number of people currently dying from road traffic accidents and cancer together.

Longer stays in hospitals means increased costs for care. The World Bank anticipates that by 2050, AMR could precipitate healthcare costs to surge by up to US$ 1 trillion, with annual GDP losses ranging between US$ 1 trillion and US$ 3.4 trillion by 2030.

Resistell aims to address these challenges head-on with the fastest and most extensible AST Platform in the world. The Resistell Multistar delivers results in just 2 hours, enabling doctors to make informed decisions faster, and ensuring patients receive the most effective treatment sooner.
